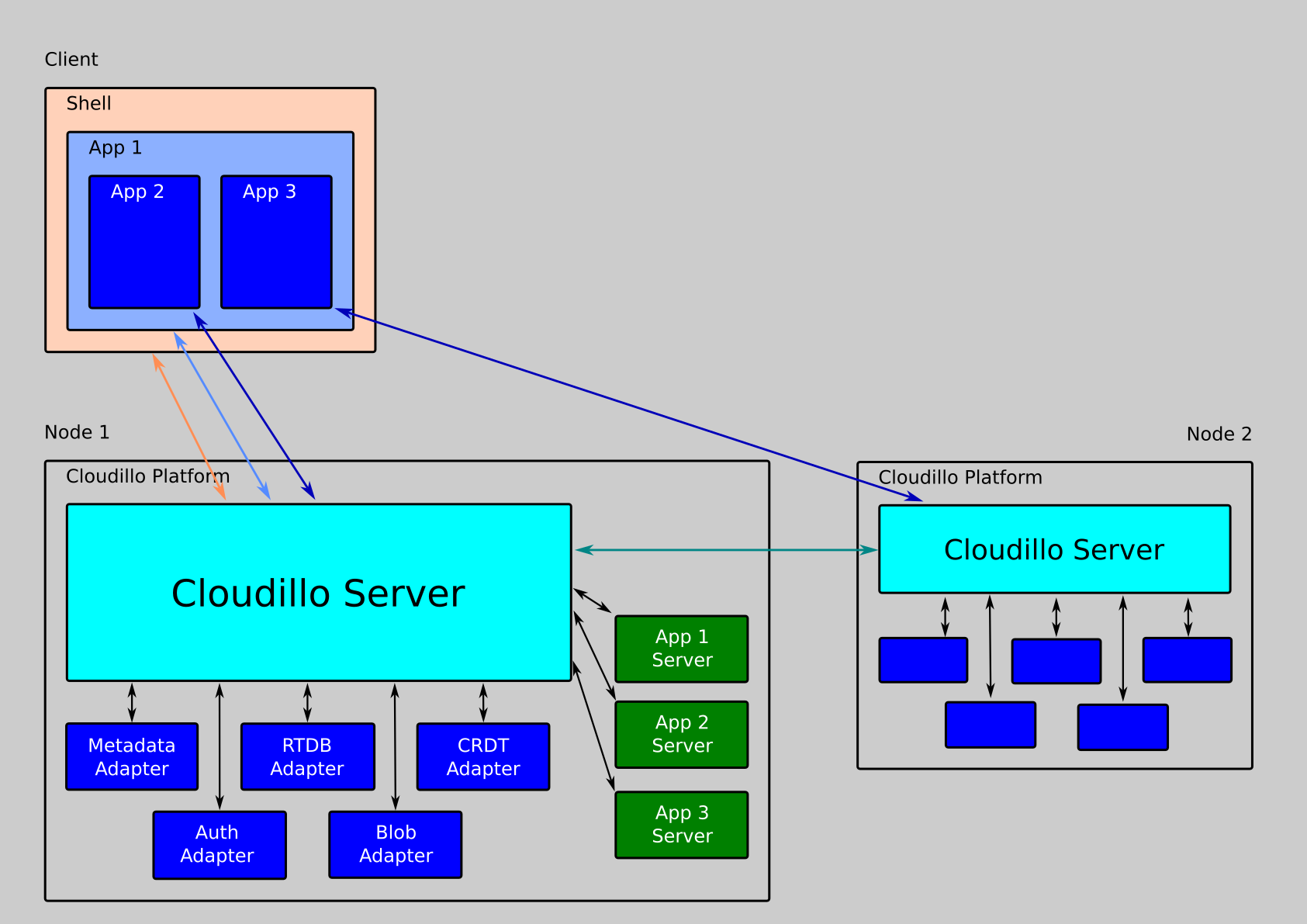
Core Concept & Architecture
Cloudillo is an open-source collaboration platform that allows users to store their own data wherever they choose. Users can:
- Self-host their data
- Store data with community-hosted servers
- Use third-party storage providers offering Cloudillo as a service
This ensures privacy-conscious users maintain full control while enabling seamless onboarding for less technical users. The design also ensures full user autonomy, preventing vendor lock-in by allowing seamless migration between storage providers or self-hosting at any time.
Architecture Diagram
Identity System & User Profiles
Cloudillo decouples identity from storage through a Domain Name System (DNS)-based identity system. Each user and community has a stable, trusted identifier independent of storage location.
Users can create identities using their own domain name, allowing them to maintain full control and leverage their trusted brand within the platform.
Cloudillo Identity Providers (CIP) help users create and manage identities without manual DNS setup. Any domain owner can implement a CIP, with the first provider being cloudillo.net.
Each Cloudillo Identity has a publicly accessible profile containing:
- Identity Name
- Identity Public Key
- Optional additional metadata
The Identity Public Key verifies user authenticity within the Cloudillo network.
Content-Addressing & Merkle Trees
Cloudillo uses content-addressing throughout its architecture, where every action, file, and data blob is identified by the cryptographic hash of its content. This creates a merkle tree structure that provides:
- Cryptographic proof of authenticity: Anyone can verify content integrity
- Immutability: Content cannot be modified without changing its identifier
- Tamper-evidence: Any modification is immediately detectable
- Deduplication: Identical content produces identical identifiers
- Trustless verification: No need to trust storage providers
Every resource in Cloudillo—from action tokens to image blobs—is part of this merkle tree, creating a verifiable chain of trust from user actions down to individual bytes of data.
Learn more: Content-Addressing & Merkle Trees
Actions
Cloudillo supports event-driven communication between nodes. Actions are event-driven interactions that users perform, such as:
- Connecting with another user
- Following a user
- Posting, commenting, or reacting
- Sharing a document
When an action occurs, Cloudillo generates a cryptographically signed Action Token, distributing it to involved parties. This mechanism prevents spam and unauthorized actions.
Action tokens are content-addressed, meaning each action has a unique identifier derived from the hash of its content. This ensures actions are immutable and verifiable.
Access Control & Resource Sharing
When a user wants to access a resource stored on another node (e.g., editing a document hosted by another user), the following process occurs:
- The user’s node requests access using their Identity Key.
- The remote node validates the request and grants an Access Token.
- The application uses this token to interact with the resource on behalf of the user.
This process ensures secure, decentralized access control without requiring direct trust between storage providers. This process is designed to be seamless, requiring no additional user interaction—offering the ease of centralized cloud platforms while maintaining full decentralization.
Authentication & Authorization Tokens
Cloudillo utilizes cryptographic tokens for authentication and authorization:
- Action Tokens: Signed by users, representing their activities (e.g., posting, following).
- Access Tokens: Used for resource access, granted by the data owner’s node.
- Verification: All tokens are cryptographically signed and validated by the recipient nodes before processing.
Resource Types & Storage Model
Cloudillo supports multiple resource types:
- Extensible Actions: Developers can define new action types that integrate seamlessly with Cloudillo’s decentralized architecture, allowing for future expansion of platform capabilities.
- Immutable Resources: Content such as images, videos, and published documents. These are content-addressed using cryptographic hashes to ensure integrity and enable deduplication.
- Editable Documents: Built-in collaborative structures allow real-time multi-user editing of documents.
- Databases: Cloudillo provides a real-time database API, enabling developers to create custom applications on top of the platform.
This design ensures Cloudillo remains flexible and adaptable to evolving user and developer needs.
Architectural Documentation
Dive deeper into Cloudillo’s architecture:
Fundamentals
- System Architecture Overview - Core patterns, adapters, and task system
- Identity System - DNS-based identity and profile keys
- Content-Addressing & Merkle Trees - How cryptographic hashing creates proof of authenticity
- Network & Security - Network architecture and security considerations
Data Storage & Access
- File Storage & Processing - Content-addressed file storage with variants
- Real-Time Database - Hierarchical JSON database with subscriptions
- Access Control - Token-based authentication and authorization
- ABAC Permissions - Attribute-based access control
Actions & Federation
- Actions & Action Tokens - Event-driven interactions and action types
- Federation Architecture - Decentralized federation and inter-instance communication
Runtime Systems
- Task Scheduler - Persistent task execution and scheduling
- Worker Pool - CPU-intensive task processing
- WebSocket Bus - Real-time notifications and presence tracking